Environment Class 13
OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS (05:26 PM)
LAND DEGRADATION (05:30 PM)
- Slight degradation: Upto 10% decrease in fertility
- Moderate degradation: 10 -50 % decrease in fertility.
- Severe degradation: More than 50 % decrease in fertility.
- REASONS
- ANTHROPOGENIC
- Deforestation escalates the process of soil erosion and reduces water percolation because of which organic content in the soil is reduced.
- Overgrazing.
- Excessive extraction of groundwater.
- Mining activities
- Construction activities
- NATURAL
- Offshore trade winds.
- Cold ocean currents.
- Subsidence of air near sub-tropical high pressure belt.
- Formation of dry continental air mass.
- Position of continents
- Continental drift
- Thermohaline circulations.
- Rain shadow effect.
- El Nino southern oscillation.
- Indian Ocean Diapole.
SOIL EROSION (05:50 PM)
- Soil is made up of four layers the top soil, Subsoil, Regolith and Parent rock.
- The top layer is removed or eroded by water and wind.
- Wind which is blowing near to the surface lifts and carries the topsoil this process is called Deflation and abrasion.
- Water erosion in that region where the water is running faster, There are five types of water erosion :
- 1)Splash erosion
- The impact of the falling raindrops on the uppermost layer of the soil, The splash of the raindrops impacts or initiates the process.
- 2)Sheet erosion
- When the water has started to flow on the uppermost layer and its removal.
- 3)Rill Erosion
- It involves the development of finger-like rill.
- 4)Gully Erosion
- When water continues to flow in the rills, The rills widen and this type of erosion is called Gully erosion. Example: Chambam badland.
- 5)Slip Erosion
- The top layer of the soil is entirely washed away, left over portion is the hard soil.
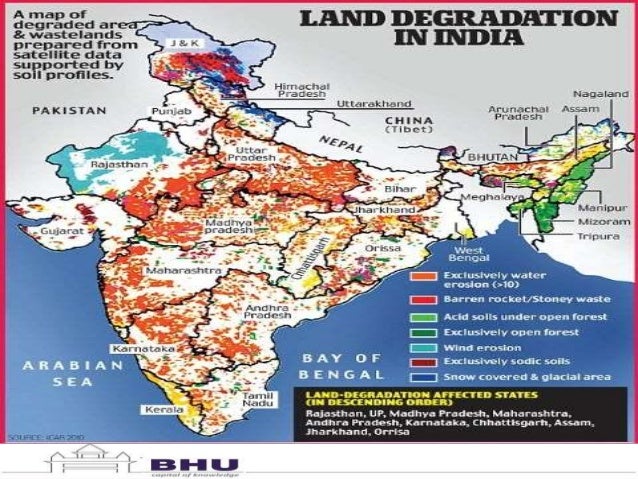
EXTENT OF LAND DEGRADATION IN INDIA (06:20 PM)
- Northern Region
- HIMALAYAS
- Because of Deforestation, Soil Erosion, Construction activities, Overgrazing, and Mass movements.
- PUNJAB HARYANA
- Because of Deforestation, Waste generation, and Waterlogging.
- RAJASTHAN AND PARTS OF GUJARAT
- Natural aridity due to low rainfall, Wind erosion, Deforestation, and Soil erosion.
- EASTERN REGION
- Basic reasons remain the same as those of the northern region.
- NORTH EAST
- Deforestation, Shifting cultivation., Water erosion,Mass movements.
-
IMPACTS OF LAND DEGRADATION (06:26 PM)
- Disturbs Ecosystem services.
- Tourism gets disturbed.
- Biodiversity loss.
- Please refer to PPT as suggested by the faculty.
METHODS OF CONSERVATION (06:35 PM)
- LAND RESTORATION
- Two methods we have Active and passive restoration.
-
ACTIVE RESTORATION PASSIVE RESTORATION - It involves the active participation of human beings to restore and reclaim the degraded land.
- No involvement of human beings in restoration and the land is left to regenerate naturally.
- Faster and costlier.
- Slower and cheaper.
- Overall quality of the restored land is better here.
- Overall quality of the restored land is poor here.
- Beneficial for the local community
- Not supportive of the local community. Rather, it negatively impacts the local community.
- Richer in Biodiversity
- Low biodiversity
- REFORESTATION & AFFORESTATION
- Recreate the forest plantation.
- AGRO-FORESTRY (06:48 PM)
- Forest inside Agriculture, wherever there is agricultural land, Plant trees there.It is Agri silviculture.
- Benefits include:
- 1)Alternative source of income through timber as well as non-timber produce like fruits, raisins etc.
- 2)Reduces soil erosion by reducing the water erosion and increasing the soil percolation.
- 3)Carbon sequestration
- 4)Reduces wind erosion also by shelter belts and windbreaks.
- 5)Increases the soil nutrients.
- 6)Allelopathy: The release of chemicals and hormones by one plant which affects the growth of another. It is used in agriculture by carefully selecting trees in agroforestry to suppress weeds, pests and insects.
- 7)Reduces the burden on the forest.
- 8)Reduces the Man-Animal conflict.
- SOCIAL FORESTRY (07:04 PM)
- Growing trees in the community land outside the conventional forest.
- JOINT FOREST MANAGEMENT (07:23 PM)
- It is the management of the forest adjacent to village areas jointly by the village community as well as the forest department.
- The village community helps the forest department in managing the forest and they are allowed to use non-timber forest produce(NTFP) through the establishment of a village forest committee.
- MULCHING
- It is the material applied on the soil surface to check soil moisture evaporation and increase soil water and nutrient availability.
- TERRACE CULTIVATION
- It involves cultivation as per the slope through step-like topography in hilly and mountainous areas to prevent soil erosion and water loss.
- CONTOUR BUNDING
- It involves the rising of bunds along contour lines to reduce soil erosion.
- MIXED CROPPING
- It involves growing different crops together at the same time.
LAND DEGRADATION NEUTRALITY (07:51 PM)
- According to UNCCD, Land degradation neutrality(LDN) is a state whereby the amount and quality of land resources necessary to support ecosystem function and services and enhanced food security remains stable or increases within specified temporal and spatial scales.
- SDG 15.3 aims to achieve LDN by 2030.
TIGER (07:58 PM)
- EFFORTS OF CONSERVATION
- 1)PROJECT TIGER
- A centrally sponsored scheme, Implemented by NTCA(National tiger conservation authority)
- There are a total of 54 tiger reserves in the country.
- NTCA is a statutory body.
- 2)TIGER CENSUS
- Coordinated exercise conducted once in four years.
- Conducted by NTCA, WWF.
- Through this the rating is also called MEETR (Management Effectiveness Evaluation of Tiger Reserves) for assessing the management of resources in the tiger reserve.
- 3)M-STRIPS(Monitoring system for Tigers intensive protection and ecological status)
- 4)CATRAT(Camera trapped data repository and analysis tool)
- INTERNATIONAL LEVEL INITIATIVE
- 1)Global tiger forum
- First-ever meeting of Tiger range countries held in New Delhi in 1993.
- 2)Global Tiger initiative
- Alliance of all the organizations of tiger conservation.
- 3)St.Peterburg summit in 2010
- Target of doubling the number of tigers in the wild by 2022.
- India is the only country to achieve this.
- 4)CA|TS (Conservation assured tiger standards)
The topic for the next class: Global Warming, Climate Change and related concepts.